DIAGNOSIS
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
• Inflammatory carcinoma;
• Advanced carcinoma with erythema, edema, and/or ulceration;
• Rarely, tuberculous abscess;
• Hydradenitis of breast skin;
• Sebaceous cyst with infection.
WORKUP
• Clinical examination sufficient;
• If abscess suspected, referral to surgeon for incision, drainage, and biopsy;
• If possible abscess or advanced carcinoma, referral for workup required.
LABORATORY TESTS
• Perform C&S test of abscess contents.
• If mammogram or ultrasound prevented by discomfort, perform after resolution of abscess if required.
TREATMENT
NONPHARMACOLOGIC THERAPY
• Established abscess: incision and drainage, preferably with general anesthesia;
• Biopsy of abscess cavity wall to exclude carcinoma.
ACUTE GENERAL Rx
• Antibiotics: the pathogen is generally staphylococci in lactational abscess. Recommended initial antibiotic therapy is with nafcillin or oxacillin 2g q4h IV or cefazolin 1g q8h IV.
• If acute mastitis is treated early, resolution without drainage is possible.
• Subareolar abscess: broad-spectrum antibiotic treatment and drainage are needed to control acute phase.
CHRONIC Rx
Further surgical treatment for recurrences or fistula
DISPOSITION
• Lactational abscess: possible to continue breast-feeding without apparent risk of infection to the infant;
• Subareolar abscess:
1. Notorious for recurrence or complication of fistula formation;
2. Patient informed and referred for subsequent care.
REFERRAL
• If abscess drainage required;
• For surgical consultation if subareolar abscess involved.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
• Inflammatory carcinoma;
• Advanced carcinoma with erythema, edema, and/or ulceration;
• Rarely, tuberculous abscess;
• Hydradenitis of breast skin;
• Sebaceous cyst with infection.
WORKUP
• Clinical examination sufficient;
• If abscess suspected, referral to surgeon for incision, drainage, and biopsy;
• If possible abscess or advanced carcinoma, referral for workup required.
LABORATORY TESTS
• Perform C&S test of abscess contents.
• If mammogram or ultrasound prevented by discomfort, perform after resolution of abscess if required.
TREATMENT
NONPHARMACOLOGIC THERAPY
• Established abscess: incision and drainage, preferably with general anesthesia;
• Biopsy of abscess cavity wall to exclude carcinoma.
ACUTE GENERAL Rx
• Antibiotics: the pathogen is generally staphylococci in lactational abscess. Recommended initial antibiotic therapy is with nafcillin or oxacillin 2g q4h IV or cefazolin 1g q8h IV.
• If acute mastitis is treated early, resolution without drainage is possible.
• Subareolar abscess: broad-spectrum antibiotic treatment and drainage are needed to control acute phase.
CHRONIC Rx
Further surgical treatment for recurrences or fistula
DISPOSITION
• Lactational abscess: possible to continue breast-feeding without apparent risk of infection to the infant;
• Subareolar abscess:
1. Notorious for recurrence or complication of fistula formation;
2. Patient informed and referred for subsequent care.
REFERRAL
• If abscess drainage required;
• For surgical consultation if subareolar abscess involved.
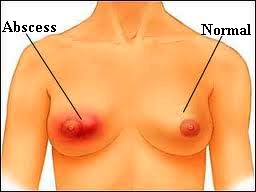
Abscess of the Breast
BASIC INFORMATION
DEFINITION
Breast abscess is an acute inflammatory process resulting in the formation of a collection of pus. Typically there is painful erythematous mass formation in the breast, occasionally with draining through the overlying skin or nipple duct opening.
SYNONYMS
Subareolar abscess;
Lactational or puerperal abscess;
Abscess of the breast;
Abscess of the nipple related to childbirth;
Abscess of the breast related to childbirth.
EPIDEMIOLOGY & DEMOGRAPHICS
• 10% to 30% of all breast abscesses are lactational.
• Acute mastitis occurs in 2.5% of nursing mothers, with 1 in 15 of these women developing abscess.
PHYSICAL FINDINGS & CLINICAL PRESENTATION
Painful erythematous induration involving the part of the breast leading to fluctuant abscess.
ETIOLOGY
• Lactational abscess: milk stasis and bacterial infection leading to mastitis, then to abscess, with Staphylococcus aureus the most common causative agent.
• 10% to 30% of all breast abscesses are lactational.
• Acute mastitis occurs in 2.5% of nursing mothers, with 1 in 15 of these women developing abscess.
PHYSICAL FINDINGS & CLINICAL PRESENTATION
Painful erythematous induration involving the part of the breast leading to fluctuant abscess.
ETIOLOGY
• Lactational abscess: milk stasis and bacterial infection leading to mastitis, then to abscess, with Staphylococcus aureus the most common causative agent.
• Subareolar abscess:
1. Central ducts involved, with obstructive nipple duct changes leading to bacterial infection.
2. Cultured organisms mixed, including anerobes, staphylococci, streptococci, and others.
1. Central ducts involved, with obstructive nipple duct changes leading to bacterial infection.
2. Cultured organisms mixed, including anerobes, staphylococci, streptococci, and others.

Contacts: lubopitno_bg@abv.bg www.encyclopedia.lubopitko-bg.com Corporation. All rights reserved.
DON'T FORGET - KNOWLEDGE IS EVERYTHING!