EARTHQUAKES AND VOLCANOES
Researchers believe that the Earth’s crust is cracked into huge pieces that fit together like a giant puzzle. The cracked sections, called tectonic plates, are supported by the oozing, soft rocks of the mantle beneath the Earth’s crust. The unstable borders between the plates are known as rings of fire. These areas are danger zones for both volcanoes and earthquakes. A volcano is an opening in the Earth’s crust which allows redhot magma (molten rock) from the mantle to escape onto the surface of the Earth. An earthquake is a shaking of the ground caused by movements of rocks beneath the Earth’s surface.
EARTHQUAKE FACT FILE
Seismologists:
Scientists who study and measure earthquakes are called seismologists.
Measuring earthquakes:
Seismologists use measuring instruments called seismographs to record the pattern of an earthquake’s seismic waves and to determine out the strength and duration of the earthquake.
The Richter scale:
The best known method of recording the magnitude of earthquakes is the Richter Scale. American seismologist, Charles F. Richter, developed this numbering system in 1935.
Earthquake depths:
The focus, the starting point, of most earthquakes is less than 50 miles below the Earth’s surface.
Largest recorded earthquake:
On May 22, 1960, an earthquake of 9.5 magnitude on the Richter Scale struck the coast of Chile, South America. Seismographs recorded seismic waves traveling around the whole world for many days afterward.

This map shows the edges of the tectonic plates that make up the Earth’s surface. The plates are constantly moving by just a few inches each year.

CONTINENTAL RIFT
The point where two continental plates
are moving apart.
The point where two continental plates
are moving apart.

VOLCANOES
Where the plates collide, magma can escape to
the surface, creating a range of volcanic mountains.
Where the plates collide, magma can escape to
the surface, creating a range of volcanic mountains.

MID-OCEAN RIDGE
NEW VOLCANIC
ISLAND
ISLAND
OCEAN TRENCH
CONTINENTAL PLATE
OCEAN PLATE
OCEAN PLATE
SUBDUCTION ZONE
Where plates collide, the edge of one is often pushed underneath the other. This is called subduction. It may take place between continental plates, ocean plates or one of each (as shown above).
Where plates collide, the edge of one is often pushed underneath the other. This is called subduction. It may take place between continental plates, ocean plates or one of each (as shown above).

SPREADING RIDGE
Lava flows out through a rift
in the ocean floor creating
new crust and a range of
undersea mountains.
Lava flows out through a rift
in the ocean floor creating
new crust and a range of
undersea mountains.
HOT SPOT VOLCANO
‘Hot spots’ are areas of great
activity in the mantle where
magma forces its way through
a tectonic plate.
‘Hot spots’ are areas of great
activity in the mantle where
magma forces its way through
a tectonic plate.
The Earth’s tectonic plate movements set off earthquakes and volcanoes, as well as create mountain ranges and deep-sea trenches.
FREQUENCY OF EARTHQUAKES WORLDWIDE
The magnitude of an earthquake is a measurement of the earthquake’s strength and size. The measuring system used here is the Richter Scale.
The intensity of an earthquake is a measurement of the shaking caused by the earthquake.
Magnitude Description Intensity Average number each year
2 to 2.9 Very minor Recorded by seismographs, but not felt by people 1,300,000
3 to 3.9 Minor Felt by some people 130,000
4 to 4.9 Light Felt by many people 13,000
5 to 5.9 Moderate Slight damage 1,319
6 to 6.9 Strong Damaging 134
7 to 7.9 Major Destructive 17
8 and higher Great Devastating 1
The magnitude of an earthquake is a measurement of the earthquake’s strength and size. The measuring system used here is the Richter Scale.
The intensity of an earthquake is a measurement of the shaking caused by the earthquake.
Magnitude Description Intensity Average number each year
2 to 2.9 Very minor Recorded by seismographs, but not felt by people 1,300,000
3 to 3.9 Minor Felt by some people 130,000
4 to 4.9 Light Felt by many people 13,000
5 to 5.9 Moderate Slight damage 1,319
6 to 6.9 Strong Damaging 134
7 to 7.9 Major Destructive 17
8 and higher Great Devastating 1
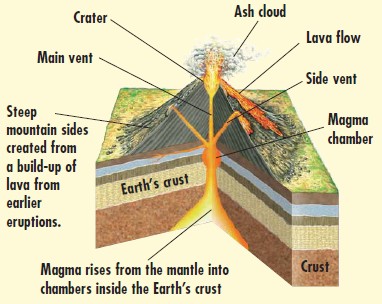
A volcano is a self-made mountain. Its hollow centre provides a pathway between the Earth’s upper mantle and the surface.
VOLCANO FACT FILE
ACTIVE OR EXTINCT?
Active volcanoes are those that erupt regularly or have the capacity to erupt. They are sometimes called dormant if they have not erupted for a very long period. Extinct volcanoes are dead volcanoes. They will not erupt again.
MAGMA/LAVA
Magma is the red-hot, melted rock inside a volcano. As soon as magma leaves a volcano and bursts out into the air or sea, it is known as lava. Lava can erupt at temperatures of up to 2192°F.
PLINIAN ERUPTIONS
During a plinian eruption, gas-rich magma explodes inside a volcano. This causes cinder, ash, and gases to be fired up into the air. sometimes as high as 19 miles!
ACTIVE OR EXTINCT?
Active volcanoes are those that erupt regularly or have the capacity to erupt. They are sometimes called dormant if they have not erupted for a very long period. Extinct volcanoes are dead volcanoes. They will not erupt again.
MAGMA/LAVA
Magma is the red-hot, melted rock inside a volcano. As soon as magma leaves a volcano and bursts out into the air or sea, it is known as lava. Lava can erupt at temperatures of up to 2192°F.
PLINIAN ERUPTIONS
During a plinian eruption, gas-rich magma explodes inside a volcano. This causes cinder, ash, and gases to be fired up into the air. sometimes as high as 19 miles!
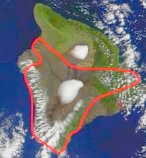
WORLD’S LARGEST VOLCANO
Mauna Loa, Hawaii, is the largest volcano on Earth. Mauna Loa last erupted in 1984. Mauna Loa’s summit is 29,527 feet from the ocean floor. However, scientists estimate that its great mass is actually squashing the ocean floor down by another 26,246 feet, giving the volcano a total height of just under 56,000 feet from seafloor base to summit.
Mauna Loa, Hawaii, is the largest volcano on Earth. Mauna Loa last erupted in 1984. Mauna Loa’s summit is 29,527 feet from the ocean floor. However, scientists estimate that its great mass is actually squashing the ocean floor down by another 26,246 feet, giving the volcano a total height of just under 56,000 feet from seafloor base to summit.
A satellite image of Mauna Loa. The volcano’s base spreads over 50% of the island of Hawaii.
STORY OF AN EARTHQUAKE
PLATE MOVEMENTS
Two tectonic plates slowly move,
squeezing and stretching the rocks
underground. Enormous pressure
builds up.
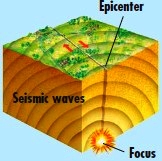
FOCUS OF THE EARTHQUAKE
Miles underground, rocks break and
give way, releasing the pressure.
The point where this happens is
called the focus or hypocenter.
SEISMIC WAVES
Vibrations, or seismic waves, are
sent out from the focus causing the
ground at the surface to shake. The
point on the surface directly above
the focus is called the epicenter.
FAULTS
Sometimes, the Earth’s crust is put
under such pressure that it cracks.
The places where the surface cracks
open are called faults. The lines the
cracks create are called fault lines.
PLATE MOVEMENTS
Two tectonic plates slowly move,
squeezing and stretching the rocks
underground. Enormous pressure
builds up.
FOCUS OF THE EARTHQUAKE
Miles underground, rocks break and
give way, releasing the pressure.
The point where this happens is
called the focus or hypocenter.
SEISMIC WAVES
Vibrations, or seismic waves, are
sent out from the focus causing the
ground at the surface to shake. The
point on the surface directly above
the focus is called the epicenter.
FAULTS
Sometimes, the Earth’s crust is put
under such pressure that it cracks.
The places where the surface cracks
open are called faults. The lines the
cracks create are called fault lines.

EARTHQUAKE AND VOLCANO DISASTERS
MOST DEADLY EARTHQUAKE
The world’s most deadly, recorded earthquake happened in 1556. The earthquake struck in central China. Around 830,000 people were killed when their homes, which were carved in soft rock, collapsed.
KRAKATOA
On August 27, 1883, the volcanic island of Krakatoa, in Indonesia, erupted in a massive explosion which could be heard across 8% of the Earth’s surface. Thousands of people were swept out to sea by a giant tsunami caused by the eruption. Over 36,000 people were killed.
EARTHQUAKES IN JAPAN
Japan is situated where four of the Earth’s plates meet. In 1923, 143,000 people were killed in the area around Tokyo, Japan’s capital, when a magnitude-8.3 earthquake struck. On January 17, 1995, a magnitude-7.2 earthquake killed 5,500 people and destroyed 100,000 homes in Kobe, Japan.
MOST DEADLY EARTHQUAKE
The world’s most deadly, recorded earthquake happened in 1556. The earthquake struck in central China. Around 830,000 people were killed when their homes, which were carved in soft rock, collapsed.
KRAKATOA
On August 27, 1883, the volcanic island of Krakatoa, in Indonesia, erupted in a massive explosion which could be heard across 8% of the Earth’s surface. Thousands of people were swept out to sea by a giant tsunami caused by the eruption. Over 36,000 people were killed.
EARTHQUAKES IN JAPAN
Japan is situated where four of the Earth’s plates meet. In 1923, 143,000 people were killed in the area around Tokyo, Japan’s capital, when a magnitude-8.3 earthquake struck. On January 17, 1995, a magnitude-7.2 earthquake killed 5,500 people and destroyed 100,000 homes in Kobe, Japan.

Contacts: lubopitno_bg@abv.bg www.encyclopedia.lubopitko-bg.com Corporation. All rights reserved.
DON'T FORGET - KNOWLEDGE IS EVERYTHING!