Table 18.1 Nomenclature of bone tumors

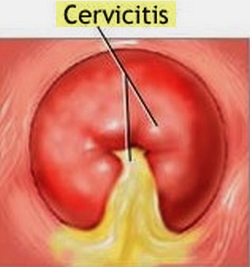
Figure 86 Colposcopy of a woman with mucopurulent cervicitis and purulent discharge from endocervical os.
DIAGNOSIS
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
• Carcinoma of the cervix
• Cervical erosion
• Cervical metaplasia
WORKUP
The patient usually presents with a vaginal discharge or history of postcoital bleeding. Otherwise the patient is diagnosed asymptomatically during routine examination. On examination there is gross visualization of yellow, mucopurulent material on the cotton swab.
LABORATORY TESTS
On a smear there will be ten or more polymorphonuclear leukocytes per microscopic field. Positive Gram stain is found. Cultures should be obtained for Chlamydia and N. gonorrhoeae. Use a wet mount to look for trichomonads. Obtain a Pap smear.
TREATMENT
NONPHARMACOLOGIC THERAPY
Cervicitis is treated in an outpatient setting. Cryosurgery is an option for treatment of cervicitis with negative cultures and negative biopsies. Safe sex should be practiced with the use of condoms. Partners should be treated in all cases of infection proven by culture.
ACUTE GENERAL Rx
Because Chlamydia and N. gonorrhoeae make up >50% of the cause of infectious cervicitis, if it is suspected, treat without waiting for culture results. Administer ceftriaxone 125-mg IM single dose followed by doxycycline 100 mg PO bid for 7 days. If the patient is pregnant, treat with azithromycin (Zithromax) 1-g single dose instead of using doxycycline, which is contraindicated in pregnant or nursing mothers. Alternative treatments include: erythromycin base 500 mg PO qid for 7 days, erythromycin ethylsuccinate 800 mg PO qid for 7 days, ofloxacin 300 mg PO bid for 7 days, or levofloxacin 500 mg PO qd for 7 days. If Trichomonas is the etiologic agent, treat with metronidazole 2-g single dose. For herpes, treat with acyclovir 200 mg PO five times daily for 7 days.
DISPOSITION
Cervicitis responds well to antibiotics. Possible complications to watch for are a subsequent PID and infertility (found in 5% to 10% of patients). Repeat cultures should be performed after treatment. Sexual relations can be resumed after negative cultures.
REFERRAL
If subsequent PID develops, consider hospital admission for IV antibiotics.
PEARLS & CONSIDERATIONS
COMMENTS
Patient educational material can be obtained from local health clinics and clinics for sexually transmitted diseases.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
• Carcinoma of the cervix
• Cervical erosion
• Cervical metaplasia
WORKUP
The patient usually presents with a vaginal discharge or history of postcoital bleeding. Otherwise the patient is diagnosed asymptomatically during routine examination. On examination there is gross visualization of yellow, mucopurulent material on the cotton swab.
LABORATORY TESTS
On a smear there will be ten or more polymorphonuclear leukocytes per microscopic field. Positive Gram stain is found. Cultures should be obtained for Chlamydia and N. gonorrhoeae. Use a wet mount to look for trichomonads. Obtain a Pap smear.
TREATMENT
NONPHARMACOLOGIC THERAPY
Cervicitis is treated in an outpatient setting. Cryosurgery is an option for treatment of cervicitis with negative cultures and negative biopsies. Safe sex should be practiced with the use of condoms. Partners should be treated in all cases of infection proven by culture.
ACUTE GENERAL Rx
Because Chlamydia and N. gonorrhoeae make up >50% of the cause of infectious cervicitis, if it is suspected, treat without waiting for culture results. Administer ceftriaxone 125-mg IM single dose followed by doxycycline 100 mg PO bid for 7 days. If the patient is pregnant, treat with azithromycin (Zithromax) 1-g single dose instead of using doxycycline, which is contraindicated in pregnant or nursing mothers. Alternative treatments include: erythromycin base 500 mg PO qid for 7 days, erythromycin ethylsuccinate 800 mg PO qid for 7 days, ofloxacin 300 mg PO bid for 7 days, or levofloxacin 500 mg PO qd for 7 days. If Trichomonas is the etiologic agent, treat with metronidazole 2-g single dose. For herpes, treat with acyclovir 200 mg PO five times daily for 7 days.
DISPOSITION
Cervicitis responds well to antibiotics. Possible complications to watch for are a subsequent PID and infertility (found in 5% to 10% of patients). Repeat cultures should be performed after treatment. Sexual relations can be resumed after negative cultures.
REFERRAL
If subsequent PID develops, consider hospital admission for IV antibiotics.
PEARLS & CONSIDERATIONS
COMMENTS
Patient educational material can be obtained from local health clinics and clinics for sexually transmitted diseases.
PHYSICAL FINDINGS
Cervicitis is usually asymptomatic or associated with mild symptoms. Copious purulent or mucopurulent in vaginal discharge (Fig. 86), pelvic pain, and dyspareunia may be present if cervicitis is severe. The cervix can be erythematous and tender on palpation during bimanual examination. The cervix may also bleed easily when obtaining cultures or a Pap smear. May have postcoital bleeding.
ETIOLOGY
• Chlamydia
• Trichomonas
• Neisseria gonorrhoeae
• Herpes simplex
• Trichomonas vaginalis
• Human papillomavirus
Cervicitis is usually asymptomatic or associated with mild symptoms. Copious purulent or mucopurulent in vaginal discharge (Fig. 86), pelvic pain, and dyspareunia may be present if cervicitis is severe. The cervix can be erythematous and tender on palpation during bimanual examination. The cervix may also bleed easily when obtaining cultures or a Pap smear. May have postcoital bleeding.
ETIOLOGY
• Chlamydia
• Trichomonas
• Neisseria gonorrhoeae
• Herpes simplex
• Trichomonas vaginalis
• Human papillomavirus
Contacts: lubopitno_bg@abv.bg www.encyclopedia.lubopitko-bg.com Corporation. All rights reserved.
DON'T FORGET - KNOWLEDGE IS EVERYTHING!
Cervicitis
BASIC INFORMATION
DEFINITION
Cervicitis is an infection of the cervix. It may result from direct infection of the cervix, or it may be secondary to uterine or vaginal infection.
Infection of the cervix must be distinguished from physiologic ectopy of columnar epithelium, which is common in young women. Mucopurulent cervicitis is characterized by a red edematous cervix with a purulent yellow discharge. The infection may result from a sexually transmitted pathogen such as Neisseria gonorrhoeae, chlamydia, or herpesvirus (which presents with vesicles and ulcers on the cervix during a primary herpetic infection), though in most cases none of these organisms can be isolated.
Mucopurulent cervicitis is an insensitive predictor of either gonorrheal or chlamydial infection and in addition has a low positive predictive value. Treatment should be based on microbiologic testing. Presumptive antibiotic treatment of mucopurulent cervicitis is not indicated unless there is a high prevalence of either N gonorrhoeae or chlamydia in the population or if the patient is unlikely to return for treatment.
SYNONYMS
Endocervicitis
Ectocervicitis
Mucopurulent cervicitis
EPIDEMIOLOGY & DEMOGRAPHICS
Cervicitis accounts for 22% to 28% of patients presenting with abnormal vaginal discharge, and this affects women only. It is most common in adolescents, but it can be found in any sexually active woman. Practicing unsafe sex with multiple sexual partners increases the risk of developing cervicitis, as well as other sexually transmitted diseases.